

Here’s a common VPN problem to watch out for: Many administrators set up their VPN servers, configure their firewalls, and discover that they still can’t connect. Most of the time you will get this Internet IP address from a subnet assigned to you by your ISP.Ī packet filtering firewall is usually placed on a router and is managed through basic access control lists, which can be challenging to configure and manage. The VPN server should have an Internet IP address on the external interface and not an internal IP address assigned by a DHCP server or hiding behind NAT. If the Internet router or any router between the firewall and the VPN server is providing NAT, it will probably break the VPN tunnel and cause your connection to fail. However, packet filtering does provide speed, simplicity, and transparency.Īnother important VPN troubleshooting tip deals with network address translation. Although a packet filtering firewall can do some blocking based on TCP and UDP port numbers, in most cases, it isn’t the best solution. Filtering involves accepting or denying TCP/IP traffic based on source and destination address of packets, TCP/UPD port utilization and other TCP/IP headers information, and specific user and computer details in advanced firewalls.Ī packet filtering firewall merely examines traffic at the network layer (Layer 3 of the OSI reference model) and accepts or rejects it based mainly on source and destination addresses. Filters come in two basic flavors:Ī firewall can engage in packet filtering, application filtering, or both. There are two types of filters and three types of firewalls to be aware of when configuring VPN connections. Understanding firewall and filter functionality However, keep in mind that having multiple services functioning on one box always involves management and troubleshooting challenges. This works nicely, since in most businesses, firewall/proxy services use more resources during the daytime hours, and VPN services use more resources during the evenings. In this case, the VPN server is still logically behind the firewall, but depending on its capability and utilization, it can complement a firewall very well, since both are essentially performing routing functions. The third option is to colocate your VPN server on the same box as your firewall. However, one vulnerability with this scenario is that the traffic between the firewall and the VPN server is not encrypted. This option also allows you to limit the resources authenticated VPN users can access on the local network by filtering their traffic at the firewall. However, if you have a dedicated VPN box that sits outside the firewall and that is only capable of sending VPN traffic through the firewall, you can limit the damage a hacker can do by hacking the VPN box. A hacker who hijacks a connection to a VPN server that is inside the firewall will be able to do some serious damage. Remember that a VPN allows users who are external to the network to feel like they are sitting on a machine inside the network. Placing a VPN server in front of the firewall can lead to greater security in some cases. However, the other two options have benefits as well.

5651 XLOG FIREWALL VPN CONFIGURATION HOW TO
Also, the administrator is already familiar with how to route traffic through the firewall and only has to become familiar with the ports needed by the VPN server. The advantage of this placement is that it fits cleanly into the network’s current security infrastructure. The thing to understand about geography and firewalls is that filtering occurs on the firewall’s external interface-the interface that connects to the Internet.Īs I mentioned above, the most common place for a VPN Server is behind the firewall, often in a DMZ with mail servers, Web servers, database servers, and so on.
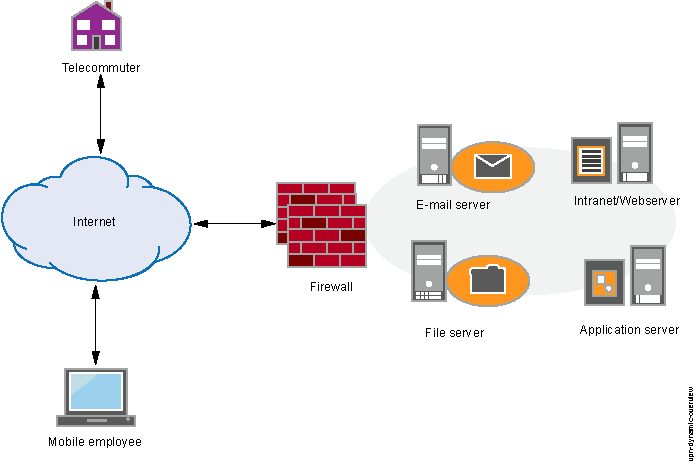
We’ll talk about filters at length in the next section. It lets you know which interfaces on the firewall will need filters assigned to them to allow VPN traffic. Geography is extremely important when configuring and troubleshooting VPN connections that pass through firewalls. The most common approach is to place the VPN server behind the firewall, either on the corporate LAN or as part of the network’s “demilitarized zone” (DMZ) of servers connected to the Internet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
